Plant Based Protein: Your Guide to Healthier Choices
Plant Based Protein: Your Guide to Healthier Choices
Plant-based protein has gained popularity as more people seek healthier dietary options. It includes proteins derived from various plant sources such as legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. This protein type offers numerous health benefits and can be a sustainable alternative to animal protein. Understanding its sources, advantages, and how to incorporate it into meals is essential for a balanced diet.
Understanding Plant-Based Protein
This section delves into the concept of plant-based protein, exploring its significance in nutrition and the reasons behind its increasing popularity.
What is Plant-Based Protein?
The term often encompasses various proteins sourced entirely from plants. These proteins derive from legumes, grains, nuts, and seeds, providing essential amino acids that contribute to a balanced diet. Unlike animal protein, plant-based options tend to offer additional health benefits due to their fiber and antioxidant content.
A variety of plant sources yield proteins that can support body functions, making it vital to understand their composition. Common sources include:
- Legumes, such as lentils and chickpeas
- Various nuts and seeds, including almonds and chia seeds
- Whole grains like quinoa and brown rice
- Soy products, notably tofu and tempeh
These sources not only provide protein but also a wealth of vitamins and minerals, enhancing overall nutritional intake.
Why Choose Plant-Based Over Animal Protein?
Opting for plant-based protein presents numerous health and environmental benefits compared to traditional animal protein sources. One significant factor is the reduced saturated fat and cholesterol levels found in most plant proteins. This can lead to better heart health and lower the risk of chronic diseases.
Environmental concerns also arise when considering animal protein production. The resources required for raising livestock are substantial, often leading to higher emissions of greenhouse gases. In contrast, plant cultivation generally requires fewer resources and contributes less to environmental degradation.
Furthermore, diets rich in plant-based proteins have been linked to:
- Lower incidence of heart disease
- Enhanced weight management
- Improved digestive health thanks to high fiber content
Shifting focus to plant-based proteins not only serves nutritional needs but also promotes a sustainable lifestyle that can positively impact the planet.
Top Sources of Plant-Based Protein
Exploring diverse sources of plant-based protein reveals a wide array of options that cater to different diets and preferences. From legumes to soy products, each source offers unique nutritional benefits.
Legumes: Beans and Lentils
Legumes are among the most abundant sources of plant-based protein. They are rich not only in protein but also in fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Common varieties include:
- Black beans
- Chickpeas
- Lentils
- Pinto beans
For instance, lentils provide around 18 grams of protein per cooked cup. Their versatility allows them to be incorporated into soups, salads, and curries seamlessly.
Nuts and Seeds
A great source of healthy fats, nuts and seeds also contribute significant amounts of protein. They can be enjoyed as snacks or used in various dishes. Noteworthy options include:
- Almonds
- Walnuts
- Chia seeds
- Hemp seeds
For example, just 100 grams of chia seeds offer about 16 grams of protein, making them a perfect addition to smoothies or oatmeal.
Whole Grains
Whole grains not only provide carbohydrates but are also valuable sources of protein. They help in maintaining energy levels while contributing to overall health. Some prominent whole grains are:
- Quinoa
- Brown rice
- Oats
- Barley
Quinoa stands out as it is a complete protein, containing all essential amino acids, and can be a fantastic base for salads or bowls.
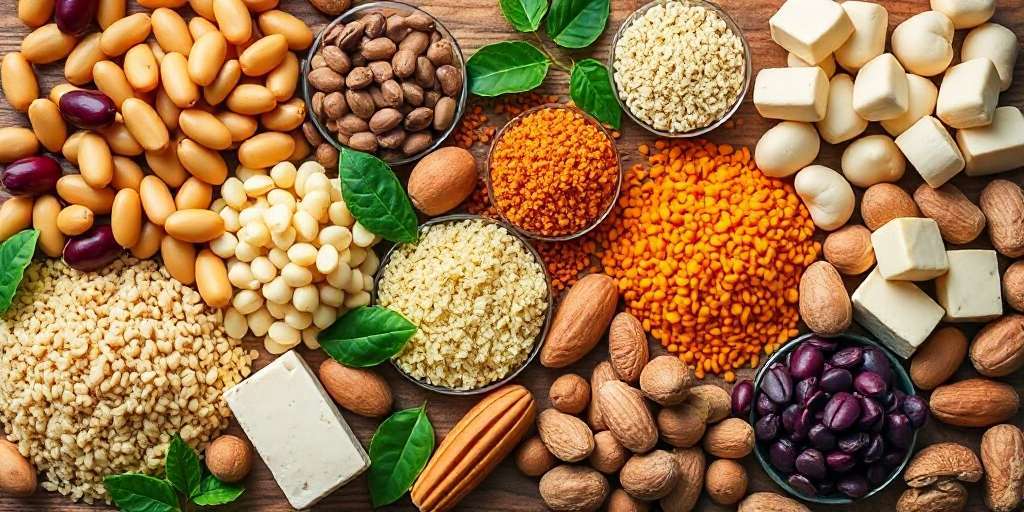

Soy Products: Tofu and Tempeh
Soy-based foods like tofu and tempeh are incredibly popular in plant-based diets. They are versatile and can mimic the taste and texture of meat. Their protein content is as follows:
- Tofu: Approximately 8 grams of protein per 100 grams
- Tempeh: About 19 grams of protein for the same serving size
Both can be used in stir-fries, sandwiches, or salads, providing a substantial protein boost.
Emerging Plant-Based Protein Sources
As the demand for plant-based options grows, new protein sources are emerging. These include:
- Pea protein
- Brown rice protein
- Insect protein (eco-friendly sources)
- Algal protein (derived from algae)
These alternatives not only address sustainability concerns but also provide unique amino acid profiles, expanding the possibilities for plant-based nutrition.
Plant-Based Protein Powders and Shakes
Powders and shakes made from plant-based proteins are becoming a popular addition to many diets. They offer convenience and can be a powerful tool for those looking to enhance their protein intake without relying on animal sources.
Choosing the Right Powder for Your Needs
When selecting a plant-based protein powder, several factors should be taken into consideration. Different powders originate from varied sources, each possessing unique qualities and benefits.
- Type of Protein: Common sources include pea, brown rice, hemp, and soy. Each type boasts distinct amino acid profiles and may cater to specific dietary preferences.
- Protein Content: It's important to check the protein content per serving as it can vary significantly between products.
- Flavor and Additives: Some powders come flavored, while others are unflavored, allowing for flexibility in incorporating them into meals. Be mindful of additives, especially sweeteners and fillers.
- Digestibility: Certain plant proteins can be easier to digest than others, so it might be worth experimenting with different types to see which works best for individual digestion.
Benefits of Protein Shakes
Integrating protein shakes into a daily routine offers numerous advantages. They serve as a quick and easy source of nutrition, particularly beneficial for busy lifestyles or post-workout recovery.
- Muscle Recovery: Consuming protein after exercise aids in muscle repair and growth, making shakes an ideal choice for athletes and fitness enthusiasts.
- Weight Management: High-protein beverages can promote satiety, potentially assisting with appetite control and healthier eating habits.
- Nutrient Boost: Many plant-based protein shakes come fortified with vitamins and minerals, providing an extra layer of nutritional support that can complement a balanced diet.
Integrating Protein Shakes into Your Diet
Incorporating protein shakes into daily meals can be straightforward and versatile. Various methods can enhance their use, making them a seamless part of a diet plan.
- Breakfast Smoothies: Adding protein powder to smoothies with fruits and vegetables can create a nourishing breakfast option.
- Baking Additions: Protein powders can be included in baking recipes for items like muffins, pancakes, or protein bars, enhancing the nutritional profile without altering taste significantly.
- Snacks: They can serve as a nutritious snack when mixed with water or plant-based milk, providing a quick protein boost between meals.
Health Benefits of Plant-Based Proteins
Exploring the health advantages associated with plant-based proteins reveals their potential to enhance well-being and prevent various ailments. These nutritional powerhouses offer compelling benefits for heart health, weight management, and digestive well-being.
Heart Health and Disease Prevention
The consumption of plant-based proteins has been linked to improved heart health. Research suggests that diets rich in plant-derived proteins contribute to lower levels of cholesterol and blood pressure. These proteins are generally lower in saturated fats compared to animal sources, leading to a reduced risk of cardiovascular diseases. Key factors include:
- Lower cholesterol levels due to the absence of animal fats.
- High fiber content that aids in reducing blood pressure.
- Rich in antioxidants, which help prevent inflammation.
Opting for a diet abundant in plant proteins can contribute significantly to long-term heart health by decreasing the likelihood of heart-related conditions.
Weight Management and Fitness
Plant-based proteins are a beneficial option for those managing their weight. They can enhance satiety and minimize overall calorie intake, making it easier to achieve and maintain a healthy weight. Foods high in protein and fiber, such as legumes and whole grains, promote fullness, thereby reducing the likelihood of overeating.
- Plant-based diets are often lower in calories, which supports weight loss efforts.
- The high fiber content contributes to improved digestion and metabolism.
- Regular consumption can help stabilize energy levels, benefiting overall fitness activity.
Incorporating these proteins into daily meals can lead to sustainable weight management while enhancing physical performance.
Digestive Health
Another benefit of plant-based proteins is their positive impact on digestive health. The rich fiber content found in many plant-based protein sources promotes regular bowel movements and maintains overall gut health. Increased fiber intake is associated with a lower risk of developing digestive disorders.
- Supports a healthy gut microbiome by serving as food for beneficial bacteria.
- Helps prevent constipation and promotes regularity.
- Contributes to the feeling of fullness, which can aid in dietary control.
A diet rich in plant-based proteins not only fuels the body but also nurtures the digestive system, fostering better gut health and improving nutrient absorption.
Plant-Based Protein and Essential Amino Acids
Understanding how to obtain essential amino acids is crucial for those embracing plant-based proteins. These amino acids are vital for various bodily functions, making it important to comprehend how they can be integrated into a plant-based diet.
Complete Proteins in a Plant-Based Diet
Complete proteins contain all nine essential amino acids that the body cannot produce on its own. While many plant-based proteins are often considered incomplete, there are several sources that contain a balanced profile of these amino acids. Notable complete protein sources include:
- Quinoa: This grain-like seed is renowned for its high protein content and includes all essential amino acids.
- Soy products: Tofu and tempeh are excellent sources of complete protein, offering high amounts of amino acids required for health.
- Chia seeds: These tiny seeds pack a punch with their protein content and provide complete amino acid profiles.
- Hemp seeds: Another nutrient-dense seed, hemp is rich in protein and complete with all essential amino acids.
Including these foods in the diet ensures adequate intake of all necessary amino acids without needing to rely solely on animal products.
Combining Foods for Amino Acid Completeness
For individuals relying primarily on plant-based proteins, it's beneficial to combine various food sources to achieve a complete amino acid profile. Certain food combinations can effectively provide the necessary building blocks for protein synthesis. Some examples of combinations include:
- Rice and beans: This classic combination not only offers complementary flavors but also balances amino acid profiles to form a complete protein.
- Peanut butter on whole grain bread: This pairing provides a diverse array of amino acids which collectively meet protein needs.
- Lentils and quinoa: By combining these two, one can enjoy a rich texture and full array of essential amino acids.
- Vegetable stir-fry with nuts: Adding nuts to a vegetable mix enhances protein intake while providing healthy fats.
It's important to note that while some foods may lack one or two essential amino acids, incorporating a variety of plant foods throughout the day can ensure that all amino acid requirements are met. This approach demonstrates that a well-rounded plant-based diet can maintain the necessary nutrients for optimal health outcomes.
Cooking with Plant-Based Proteins
Creativity in the kitchen can elevate the experience of incorporating plant-based proteins. Cooking with these ingredients offers a myriad of flavors and textures while promoting a healthy lifestyle.
Easy Recipes to Try
Plant-based proteins provide a versatile foundation for various dishes. Here are some easy recipes that can be prepared quickly while still delivering on taste and nutrition:
-
Chickpea Salad
This refreshing salad combines canned chickpeas, diced cucumbers, tomatoes, red onion, and a dollop of tahini or hummus. Season with lemon juice, salt, and pepper for a simple yet nutritious dish.
-
Quinoa & Black Bean Bowl
Cook quinoa and mix it with black beans, corn, and avocado. Top with lime juice and cilantro for a vibrant, protein-packed meal that is rich in fiber.
-
Tofu Stir-Fry
For a quick dinner, sauté cubed tofu with an array of vegetables such as bell peppers, broccoli, and snow peas. Flavor with soy sauce or teriyaki for a savory bite.
-
Lentil Soup
A hearty lentil soup can be made by simmering lentils with diced carrots, celery, and tomatoes in vegetable broth. Season with herbs like thyme and bay leaves for depth.
Tips for Delicious Plant-Based Cooking
Enhancing the flavor of plant-based dishes requires thoughtful techniques. The following tips can lead to more enjoyable and satisfying meals:
-
Use Fresh Herbs and Spices
Fresh herbs and spices can transform simple dishes and add layers of flavor. Consider using basil, cilantro, cumin, or paprika to elevate any recipe.
-
Experiment with Marinades
Marinating proteins like tofu or tempeh can enhance their taste significantly. A mixture of soy sauce, garlic, ginger, and sesame oil works well with soy products.
-
Incorporate Various Textures
To keep meals interesting, mix different textures. Combine crunchy vegetables with creamy dressings or roasted nuts to create a delightful sensory experience.
-
Don’t Be Afraid to Play with Cooking Techniques
Try grilling, roasting, or sautéing plant-based proteins. Each method brings out different flavors and can enhance overall enjoyment.
The Environmental Impact of Plant-Based Proteins
The rising interest in plant-based proteins is not only due to health benefits but also their positive effects on the environment. Sustainable practices in food production can lead to significant reductions in resource use and carbon emissions.
Sustainability and Resource Use
Plant-based proteins generally require fewer natural resources compared to animal-based proteins. The following points highlight key aspects of sustainability associated with plant proteins:
- Lower Water Usage: Producing plant-based foods often uses significantly less water than raising livestock. For instance, growing legumes and grains consumes substantially less water than beef or dairy farming.
- Reduced Land Requirements: Crops like beans and lentils can be cultivated on less land compared to the vast areas needed for cattle ranching. This efficient use of land can help safeguard natural habitats.
- Less Energy Consumption: The energy required for growing, harvesting, and processing plant foods is usually lower than that needed for animal farming. Reducing energy demand contributes to lower greenhouse gas emissions.
Reducing Carbon Footprint
One significant advantage of shifting towards plant-based diets is the potential for reducing carbon emissions. Meat production, especially beef, is a major contributor to greenhouse gases, while plant farming generates far fewer emissions. The factors influencing this reduction include:
- Lower Methane Emissions: Ruminant animals produce methane during digestion, which is a potent greenhouse gas. Plant crops do not emit methane, making them a cleaner choice.
- Decreased Fertilizer Runoff: Plant-based diets can lead to lower usage of chemical fertilizers typically associated with livestock production, which helps preserve water quality in surrounding ecosystems.
- Enhanced Soil Health: Crop rotation and planting legumes can improve soil quality, sequestering carbon and reducing dependence on synthetic additives, contributing to a healthier environment.
Common Questions About Plant-Based Proteins
This section addresses some frequently asked questions surrounding plant-based proteins, covering suitability, adequate intake on a vegan diet, and common food allergies related to plant proteins.
Are Plant-Based Proteins Suitable for Everyone?
Plant-based proteins can be appropriate for a wide range of individuals, including vegetarians, vegans, and those looking to reduce animal product consumption. However, dietary needs vary significantly from person to person. While many can thrive on a plant-based diet, it's essential to ensure a varied intake to meet nutritional requirements.
Some populations, such as pregnant or nursing women, children, and athletes, might have different protein needs. Consulting with a healthcare provider or a dietitian can provide personalized guidance. Any individual considering a significant dietary change should also take into account their health conditions or dietary restrictions.
How to Get Enough Protein on a Vegan Diet?
Ensuring adequate protein intake on a vegan diet involves selecting a diverse range of protein sources throughout the day. Individuals can focus on incorporating the following:
- Legumes such as lentils, chickpeas, and various beans.
- Nuts and seeds, including almonds, chia seeds, and hemp seeds.
- Whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and oats.
- Soy products, such as tofu and tempeh, which are protein-dense options.
Planned meals should focus on combining different protein sources to ensure that all essential amino acids are included. For example, pairing rice with beans or whole grain bread with peanut butter provides a complete amino acid profile.
Addressing Food Allergies and Sensitivities
Food allergies and sensitivities can complicate the incorporation of plant-based proteins. Some individuals may be allergic to common sources such as soy, nuts, or gluten found in products like seitan. It's important for individuals with allergies to identify safe foods and explore alternatives that can provide adequate nutrition without triggering reactions.
For those who can't consume soy products, alternatives such as legumes or certain grains may provide similar benefits. It's crucial to read labels carefully and consider cross-contamination if purchasing packaged products.
In the case of gluten sensitivities, many whole grains can still be enjoyed, including quinoa, millet, and rice. By understanding personal dietary needs and preferences, one can navigate plant-based protein options effectively while maintaining a balanced diet.
Making the Transition to a Plant-Based Diet
Transitioning to a plant-based diet can be an enriching experience that promotes health and sustainability. A strategic approach can simplify this shift and enhance enjoyment of diverse foods.
Tips for Beginners
Embarking on this journey requires thoughtful planning and experimentation. The following strategies can ease the process and make it more enjoyable:
- Start gradually: Begin by incorporating more plant-based meals instead of completely overhauling the diet. Replace one meal a day with a plant-based option to adjust over time.
- Explore new recipes: There is a wealth of delicious plant-based recipes available. Experimenting with different cuisines can reveal exciting flavors and textures.
- Focus on whole foods: Prioritize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. These provide essential nutrients and contribute to overall wellness.
- Plan meals: Developing weekly meal plans can help ensure a variety of nutrients are consumed. This also simplifies grocery shopping and meal prep.
- Join a community: Connecting with others on a similar journey can provide support, motivation, and new ideas. Online forums and local groups are great places to share experiences.
Staying Motivated on a Plant-Based Lifestyle
Maintaining enthusiasm for a plant-based lifestyle can be challenging but is vital for long-term adherence. The following tips can help sustain motivation:
- Track progress: Keeping a journal of meals and experiences can provide encouragement and help pinpoint favorites or areas that need adjustment.
- Set realistic goals: Establishing achievable short- and long-term goals can help maintain focus and create a sense of accomplishment.
- Celebrate milestones: Acknowledging personal achievements, whether trying a new recipe or reaching a month of adherence, reinforces positive behavior.
- Stay informed: Reading books, watching documentaries, or following nutrition blogs can provide new insights and inspiration regarding plant-based nutrition.
- Incorporate variety: Mixing up the diet and exploring seasonal produce can prevent monotony and enhance excitement for meals.
Final Thoughts on Plant-Based Proteins
The expanding interest in plant-based proteins highlights the evolving dietary preferences of many individuals. More people are discovering their significance not just for personal health, but for the environment as well.
Embracing a Healthier Lifestyle
Transitioning to a diet rich in plant-based proteins can lead to numerous health benefits. This lifestyle choice often emphasizes whole foods that are nutritious and packed with essential vitamins and minerals. Incorporating these proteins can contribute to:
- Improved heart health through reduced cholesterol levels.
- Weight management facilitated by higher fiber content that promotes satiety.
- Enhanced digestive health with increased fiber intake.
Ultimately, the shift towards plant-based living supports overall well-being and reduces the likelihood of chronic diseases. Such a diet encourages mindful eating and a deeper connection to food sources. The choices made today can significantly influence long-term health outcomes.
The Future of Plant-Based Nutrition
The landscape of plant-based nutrition is constantly evolving, driven by research, innovation, and sustainability needs. As consumer knowledge grows, manufacturers are responding by offering a wider variety of plant-derived protein products. This evolution will likely lead to:
- Continued development of high-quality protein sources.
- Increased availability of fortified plant products, catering to nutritional gaps.
- Heightened focus on eco-friendly farming practices to support sustainable agriculture.
Looking ahead, the integration of plant-based proteins into mainstream diets has the potential to reshape nutritional guidelines. With greater emphasis on environmental sustainability, plant-based diets will likely not only become more popular but also more accessible to diverse populations.
The connection between nutrition and ecological impact is coming to the forefront, emphasizing the importance of choosing plant-based options that benefit both health and the planet. This dynamic interplay will continue to shape the future of dietary choices in the years to come.