Immune Health Products: Boost Your Immunity Naturally
Immune health products play a crucial role in supporting the body's natural defenses against infections. These products often include vitamins, minerals, and botanical supplements that promote overall immune function. Many people seek these supplements to enhance their resilience and well-being. Understanding the key ingredients and their benefits can help individuals make informed choices for maintaining a healthy immune system.
Understanding Immune Health and Its Importance
Immune health plays a crucial role in overall well-being, serving as the body's defense mechanism against various pathogens. This section explores the immune system's functions, the factors influencing its performance, and the differences between innate and adaptive responses.
The Role of the Immune System in Preventing Infections
The immune system is a complex network that includes cells, tissues, and organs working together to safeguard the body from infections. Its primary functions include identifying and neutralizing harmful invaders such as bacteria, viruses, and parasites. This defense mechanism operates through several key components:
- White Blood Cells: These cells are crucial in recognizing and responding to pathogens. Different types of white blood cells, including neutrophils, lymphocytes, and macrophages, play distinct roles in the immune response.
- Antibodies: Produced by B cells, antibodies bind to specific antigens on pathogens, marking them for destruction.
- Cytokines: These signaling proteins mediate communication between immune cells, helping to recruit additional defenders to sites of infection.
Factors Affecting Immune Function
Various factors can influence the immune system's efficiency, impacting its ability to prevent infections:
- Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in essential vitamins and minerals is vital for optimal immune function. Deficiencies in key nutrients can weaken immune responses.
- Stress: Chronic stress has been shown to impair immune function, making the body more susceptible to illness.
- Sleep: Quality sleep is essential for maintaining a robust immune system. Sleep deprivation can negatively affect immune cell production and function.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise is associated with improved immune health, promoting better circulation and enhancing the body's ability to fight infections.
Immune Response: Innate vs Adaptive Immunity
The immune response can be divided into two distinct yet interconnected systems: innate and adaptive immunity. Each plays a unique role in the body's defense strategies.
Innate Immunity
Innate immunity acts as the body’s first line of defense against pathogens and is characterized by:
- Immediate Response: This system responds rapidly to infections, typically within hours.
- Non-Specific Mechanisms: Innate immunity recognizes general features of pathogens rather than specific antigens, utilizing barriers like skin, mucous membranes, and various immune cells.
Adaptive Immunity
Adaptive immunity develops more slowly but provides a targeted and long-lasting defense:
- Specific Response: This system recognizes and remembers specific pathogens, allowing for a more efficient response upon re-exposure.
- Memory Cells: After an initial infection, the adaptive immune system creates memory cells that can quickly mobilize during subsequent exposures to the same pathogen.
Key Nutrients That Support Immune Health
A variety of essential nutrients plays a significant role in supporting and enhancing immune function. Understanding these nutrients can help in choosing dietary and supplemental options that contribute to a robust immune system.
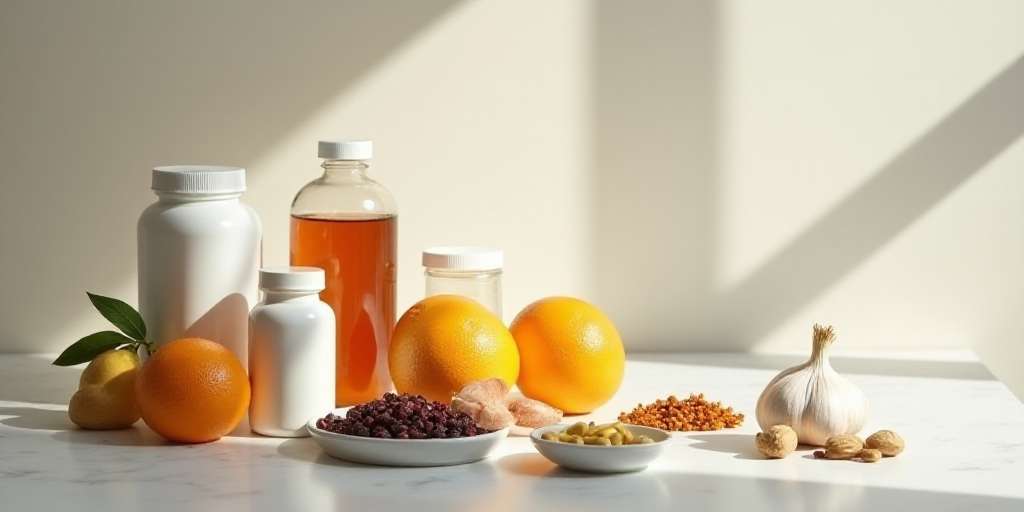

Vitamins Essential for Immune Support
Vitamin C and Its Effect on Immune Cells
This powerful antioxidant is crucial for the proper functioning of immune cells. Vitamin C enhances the activity of phagocytes, which are essential for engulfing pathogens. It also promotes the proliferation of lymphocytes, improving the body's ability to fight infections. Regular intake of this vitamin can lower the duration and severity of colds and respiratory infections.
Vitamin D’s Role in Modulating Immune Responses
Vitamin D is vital for immune system regulation. It helps to modulate the immune responses, reducing inflammation and supporting defenses against infections. Studies have shown that adequate levels of vitamin D can enhance the pathogen-fighting effects of monocytes and macrophages, critical components of the innate immune system.
Vitamin A in Maintaining Mucosal Barriers
Vitamin A is essential for maintaining mucosal surfaces, which serve as the first line of defense against pathogens. This vitamin plays a significant role in the formation and maintenance of epithelial tissues and mucous membranes. A deficiency can lead to increased susceptibility to infections, highlighting the importance of sufficient dietary sources.
Vitamin E and Antioxidant Protection
Vitamin E functions as a powerful antioxidant that protects immune cells from oxidative stress. It supports the immune system by improving the function of T cells and enhancing the body's ability to fight off infections. Supplementing with vitamin E may particularly benefit older adults, whose immune response may be diminished.
Essential Minerals for Immune Function
Zinc’s Impact on T Cell Development
This mineral is fundamental for the development and function of immune cells, particularly T lymphocytes. Zinc deficiency can lead to impaired immune cell function and increased risk of infections. Ensuring adequate zinc intake helps support cellular responses, signaling, and overall immune health.
Selenium and Antioxidant Defense Mechanisms
Selenium is known for its antioxidant properties, which help combat oxidative stress within the body. This mineral supports the immune system by enhancing the activity of immune cells and providing protection against viral infections. Research indicates that selenium deficiency may lead to reduced immune responses and increased susceptibility to diseases.
Fatty Acids and Immune Modulation
EPA and DHA Benefits for Immune Health
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, play a crucial role in modulating immune responses. These fatty acids are known for their anti-inflammatory properties, which can help in maintaining a balanced immune response. They contribute to improved cell membrane function in immune cells, enhancing their effectiveness in fighting pathogens. Regular consumption of sources rich in EPA and DHA, such as fish oil, can promote overall immune health.
Botanical and Natural Supplements for Immune Support
These supplements play a pivotal role in supporting immune health. Derived from various plants and natural sources, they offer diverse benefits that contribute to overall wellness.
Echinacea and Respiratory Tract Infection Prevention
Echinacea is widely recognized for its supportive role in preventing respiratory infections. Traditionally used by Native Americans, this herb has gained popularity as a complementary treatment for the common cold and flu. Research indicates that echinacea may reduce the likelihood of developing colds by enhancing immune function.
The key components in echinacea are believed to stimulate the production of white blood cells, the body’s first line of defense. Some studies suggest that taking echinacea at the onset of cold symptoms can decrease their duration and severity, helping individuals recover more quickly.
Elderberry Extract for Cold and Flu Symptoms
Elderberry is another botanical known for its immune-supporting properties. Rich in antioxidants, elderberry extract has been found to possess antiviral effects, particularly against influenza viruses. Clinical trials have shown that this natural remedy can help alleviate cold and flu symptoms by shortening their duration and reducing severity.
The flavonoids present in elderberries are responsible for their health-promoting attributes. They aid in inhibiting the replication of viruses, allowing the immune system to respond more effectively. Elderberry syrup or capsules are popular forms of supplementation, making it easy to incorporate into daily routines.
Garlic’s Antimicrobial and Immune-Boosting Effects
Garlic has long been hailed for its various health benefits, particularly its ability to enhance immune function. The active compound, allicin, has demonstrated antimicrobial properties, enabling the body to fend off infections more effectively. Research suggests that garlic may reduce the severity of colds and improve overall immune response.
Consuming raw or cooked garlic regularly can boost the body’s defenses. Its anti-inflammatory effects further contribute to its status as a powerful immune-supportive agent, making it a valuable addition to a healthy diet.
Green Tea and Its Immune-Enhancing Properties
Green tea is renowned for its high content of catechins, a type of antioxidant that supports immune health. These compounds are known to enhance the function of immune cells and help protect against infections. Drinking green tea regularly can improve overall health and bolster the body’s defense mechanisms.
Furthermore, green tea has anti-inflammatory properties that may contribute to reducing the risk of developing certain diseases. Its ability to help regulate immune responses makes it a beneficial beverage for those looking to maintain a strong immune system.
Probiotics and Gut-Immune System Connection
Probiotics are microorganisms that provide numerous health benefits, especially for gut health. Emerging research has shown that a healthy gut microbiome is crucial for an effective immune response. Probiotics can help modulate immune functions, thereby preventing infections and promoting overall wellness.

Strains That Affect Immune Responses
Various strains of probiotics have demonstrated the ability to enhance immune responses. For instance, Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium strains are often studied for their positive effects on the immune system. They contribute to the production of antibodies and other immune-boosting compounds, providing significant support during times of illness.
Clinical Trials on Probiotics and Respiratory Health
Clinical trials have explored the impact of probiotics on respiratory health, particularly regarding seasonal illnesses. Numerous studies suggest that individuals who take probiotic supplements are less likely to experience respiratory infections and report milder symptoms if they do get sick. This highlights the importance of gut microbiota in supporting the immune system.
Dietary Sources and Immune System Booster Foods
Incorporating a variety of foods that bolster the immune system is essential for maintaining optimal health. A well-rounded diet filled with specific nutrients can support the body's defenses against infections and enhance overall wellness.
Foods Rich in Immune-Supportive Vitamins and Minerals
Several foods are particularly beneficial due to their high content of vitamins and minerals that play crucial roles in immune function. These nutrients help improve the body's ability to combat infections and diseases.
- Citrus Fruits: Rich in vitamin C, fruits such as oranges, lemons, and grapefruits are fantastic for immune function. Vitamin C supports the production of white blood cells, which are critical for fighting infections.
- Green Leafy Vegetables: Spinach, kale, and swiss chard are loaded with vitamins A, C, and K. These nutrients are vital for maintaining healthy mucosal barriers and overall immune health.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, sunflower seeds, and walnuts provide vitamin E and zinc, which are essential for immune cell function and antioxidant protection.
- Seafood: Fatty fish like salmon and sardines are sources of omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin D, both of which help modulate immune responses and reduce inflammation.
- Garlic: Known for its antimicrobial properties, garlic can enhance the response of immune cells and is a flavorful addition to various dishes.
Incorporating Immune-Boosting Foods into Daily Diet
When it comes to enhancing immune support through diet, consistency and variety are key. Making small adjustments to meals can lead to significant health benefits.
- Start with Breakfast: Consider adding spinach or kale to smoothies, or enjoy a fruit-packed yogurt topped with nuts and seeds for a nutrient-rich meal.
- Flavor with Herbs and Spices: Use garlic, ginger, and turmeric in cooking to not only enhance flavor but also boost immunity.
- Snack Wisely: Choose snacks like almonds or carrot sticks with hummus instead of processed options. This boosts nutrient intake without added sugars or unhealthy fats.
- Make Soup Broths: Homemade broths can be enriched with vegetables and herbs to create a nourishing meal that supports immune health.
The Role of Diet Diversity for Optimal Immune Function
A diverse diet ensures a wide range of nutrients that help support the immune system effectively. Different foods offer unique benefits that work synergistically to maintain health.
Variety not only helps in obtaining essential vitamins and minerals but also contributes to the gut microbiome. A healthy gut is crucial for immune function as it hosts beneficial bacteria that play a role in immune responses.
- Eat a Rainbow: Aim to incorporate colorful fruits and vegetables into daily meals to benefit from various phytochemicals and antioxidants.
- Rotate Protein Sources: Alternate between plant-based proteins like beans and legumes and animal sources like fish and poultry to maximize nutrient intake.
- Explore Whole Grains: Include whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and oats for fiber, which supports gut health and, in turn, immune function.
Immune Support Supplements: Selection and Use
Understanding the various types of immune support supplements available and how to use them effectively is essential for promoting overall immune health.
Types of Immune Health Supplements Available
There are numerous immune health supplements on the market, each offering distinct benefits tailored to individual needs.
Multivitamins with Immune-Enhancing Formulas
Multivitamins that specifically target immune support combine a range of essential vitamins and minerals. These often include key nutrients like Vitamin C, Vitamin D, and zinc, which are known to play a significant role in enhancing immune function. A well-rounded multivitamin may provide a convenient way to ensure one gets the necessary nutrients for optimal immune health.
Single-Nutrient Supplements: When and Why to Use Them
In some cases, individuals may require higher doses of specific nutrients that can be achieved through single-nutrient supplements. For example, Vitamin D may be particularly beneficial for those who have limited sun exposure, while zinc supplements can help if there is a deficiency affecting immune response. Using these supplements wisely can target specific needs and enhance overall health outcomes.
Considerations for Supplement Quality and Purity
Quality and purity of supplements are vital factors in ensuring their effectiveness and safety. It is essential to choose products from reputable companies that adhere to strict quality control standards. Look for certifications such as Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) or third-party testing, which can provide assurance that the product contains what it claims without harmful contaminants.
Recommended Dosages and Supplementation Guidelines
Supplement dosages can vary greatly depending on individual health needs and the specific product used. It is crucial to follow the manufacturer's recommendations and consider factors such as age, health status, and lifestyle when determining appropriate dosages. Consulting with a healthcare professional for personalized advice can be beneficial when incorporating immune support supplements into one’s routine.
Age-Specific Supplement Needs: Children vs Adults
Different age groups have distinct nutritional requirements. Supplements designed for children typically contain lower doses of certain nutrients to suit their growing needs, while adult formulations may focus on more concentrated dosages to combat age-related decline in immune function.
- Children: Formulations for young individuals often include essential vitamins and minerals to support their developing immune systems and should be taken as recommended by pediatricians.
- Adults: Adults may require a broader spectrum of nutrients to address aging and lifestyle factors affecting immunity, emphasizing the importance of regular supplementation tailored to their specific health challenges.
Clinical Evidence and Research on Immune Supplements
The exploration of immune supplements has expanded significantly in recent years. Research studies, including systematic reviews and controlled trials, provide valuable insights into the efficacy of various nutrients and botanicals in enhancing immune health.
Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses on Vitamins and Minerals
Systematic reviews and meta-analyses reflect a comprehensive examination of available studies. They aggregate data from multiple trials to assess the overall effectiveness of vitamins and minerals on immune function. Several reviews emphasize the importance of certain nutrients, particularly vitamin C, vitamin D, and zinc, in boosting immune responses and reducing infection risk.
- Consistent evidence suggests that vitamin C aids in the proliferation and function of immune cells, supporting the body in fighting off pathogens.
- Vitamin D has been shown to play a role in the regulation of immune responses and may reduce susceptibility to respiratory infections.
- Zinc contributes to the development of T lymphocytes, crucial for adaptive immunity.
Randomized Controlled Trials on Supplementation Effects
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are pivotal in understanding the specific effects of immune supplements. They provide robust evidence regarding the impact of supplementation on health outcomes.
Impact on Acute Respiratory Tract Infections
Research indicates that supplementation with vitamins such as C and D can significantly lower the incidence of acute respiratory tract infections. RCTs have shown that individuals receiving these nutrients reported fewer infections compared to those on a placebo.
Effects on Duration and Severity of the Common Cold
Investigations focusing on the common cold have noted that regular intake of vitamin C can decrease the duration of cold symptoms. Moreover, studies have found that individuals taking vitamin D regularly experienced a reduction in both the frequency and severity of cold infections.
Research on Supplementation in Populations With HIV
In vulnerable populations, particularly those with HIV, research has indicated that specific nutrient supplementation can bolster immune function. Studies demonstrate that micronutrient deficiencies are common in individuals with HIV, and supplementation may help in managing the disease and improving overall immune responses.
- Supplementing with vitamins A, C, and E has shown positive effects on immune markers in these populations.
- Overall, proper nutritional support is crucial for optimizing health outcomes in individuals living with HIV.
The Role of Supplements in COVID-19 and Immune Health
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to heightened interest in the relationship between immune health and nutrient supplementation. Research has explored whether supplements could aid in the prevention or mitigation of viral infections.
- Several studies suggest that adequate levels of vitamin D may be linked to lower rates of severe complications from COVID-19.
- Emerging data also indicate that zinc supplementation could play a role in reducing viral replication and modulating the immune response during infections.
Potential Risks and Limitations of Immune Supplement Use
While immune supplements can offer benefits, it is critical to acknowledge their potential risks and limitations for informed decision-making.
Common Myths and Misconceptions
Understanding immune supplements requires debunking prevalent myths surrounding their efficacy and safety. Many people believe that taking higher doses of supplements can drastically enhance immune response, which is often not the case. Supplements do not provide a magical solution to health; they are meant to complement a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle.
Another misconception is that all natural supplements are inherently safe. In reality, just because a product is labeled "natural" does not guarantee it is free from side effects or potential interactions with other medications. Individuals often mistakenly think they can rely on supplements alone without maintaining dietary variety and a healthy lifestyle.
Risks of Over-Supplementation and Toxicity
Over-supplementation can lead to toxicity, which poses serious health risks. Vitamins and minerals, when consumed in excess, can accumulate in the body and cause adverse effects. For instance, excess vitamin A may lead to liver damage, while high doses of vitamin D can result in hypercalcemia, affecting kidney function.
- Vitamin A: Risk of toxicity includes headaches, dizziness, and liver damage.
- Vitamin D: Over consumption can lead to dangerously high calcium levels, resulting in nausea and kidney stones.
- Zinc: Excess can cause nausea, diarrhea, and interfere with the absorption of other essential minerals.
Understanding recommended dietary allowances (RDAs) and tolerable upper intake levels (ULs) is essential for safe supplementation. It is crucial for individuals to be aware of total nutrient intake from both supplements and food sources to avoid dangerous levels.
Interaction with Medications and Health Conditions
Immune supplements can interact with prescription and over-the-counter medications, potentially reducing their effectiveness or increasing side effects. For example, high doses of vitamin E may interfere with blood-thinning medications, increasing the risk of bleeding. Likewise, certain herbal supplements can affect the metabolism of various drugs.
People with existing health conditions should consult healthcare providers before starting any supplemental regimen, as certain ingredients may exacerbate chronic issues or complicate treatment protocols.
Supplements That Did Not Show Significant Immune Benefits
While many immune health products claim to enhance immunity, scientific evidence supporting their efficacy can vary significantly. Certain supplements have not demonstrated significant benefits in clinical trials, leading to skepticism about their intended use. For instance, some studies have shown that popular supplements such as elderberry may have limited effects on respiratory infections compared to the broad claims made by manufacturers.
Critical evaluations of products claiming immune support reveal that not all supplements yield positive results. Some marketing strategies may exaggerate benefits, causing consumers to invest in products without substantial scientific backing.
Guidelines from Health Professionals and Regulatory Bodies
Health professionals and regulatory bodies provide guidelines to empower consumers with reliable information regarding the safe use of supplements. These guidelines are critical for ensuring informed choices in the pursuit of improved immune health.
Fact Sheets and Recommendations From Health Authorities
Various health authorities, including the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the National Institutes of Health (NIH), develop fact sheets and guidance documents concerning dietary supplements. These documents typically offer:
- Information about essential vitamins, minerals, and their recommended daily values.
- Instructions on how these nutrients contribute to immune function and overall health.
- Advice on potential interactions with medications or negative effects when consumed in excess.
These resources serve to inform the public and healthcare professionals about evidence-based practices related to supplementation, helping individuals make choices aligned with scientific research.
Role of Healthcare Providers in Supplement Advice
Healthcare providers play a pivotal role in guiding patients regarding the use of immune health products. Their expertise can help consumers navigate the often-overwhelming array of supplements available. Key aspects of their involvement include:
- Assessing individual health needs and determining suitable supplements based on medical history.
- Providing personalized recommendations that align with dietary habits and lifestyle factors.
- Monitoring the effects of supplementation over time to ensure efficacy and safety.
By working collaboratively with healthcare providers, consumers can better understand the role of supplements in their immune health strategy, maximizing the benefits while minimizing risks.
Regulatory Standards for Dietary Supplements in the United States
The regulation of dietary supplements in the United States falls under the jurisdiction of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Although supplements are not evaluated as rigorously as pharmaceutical drugs, there are several important regulations in place:
- Manufacturers must ensure their products are safe and accurately labeled, without misleading claims.
- Good manufacturing practices (GMP) must be followed to maintain product quality and purity.
- The FDA has the authority to take action against any supplement containing harmful ingredients or making false claims.
These regulatory frameworks are designed to protect consumers by ensuring that supplements are manufactured to certain standards, thereby fostering public confidence in the safety and efficacy of immune health products.
Disclaimer and Responsible Use of Immune Health Products
Understanding the responsible usage of immune health products is vital for maximizing their benefits while minimizing potential risks. This section discusses important considerations for supplement use.
Importance of Combining Supplements With Healthy Lifestyle
To achieve optimal health, immune health products should complement a balanced lifestyle rather than serve as a substitute. A robust immune system relies heavily on a variety of factors including:
- Nutritious diet filled with fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Regular physical activity which contributes to overall health and wellness.
- Adequate sleep, essential for recovery and immune function.
- Effective stress management techniques, as chronic stress can weaken immune responses.
Incorporating these elements into daily routines can enhance the effectiveness of supplements, aiding in the overall maintenance of a healthy immune system.
When to Seek Professional Medical Advice
Consulting with healthcare providers is crucial when considering immune health supplements, specifically when:
- Starting a new supplement regimen, especially for individuals with pre-existing health conditions.
- Taking prescription medications to avoid potential interactions.
- Addressing specific health concerns or symptoms that may require medical attention.
Healthcare professionals can provide personalized advice tailored to individual health profiles, ensuring that supplement use aligns with overall wellness goals.
Understanding Supplement Limitations and Evidence-Based Use
While many immune health products have been researched, it is essential to recognize their limitations. Not all supplements work the same for everyone, and their effectiveness can vary based on various factors including:
- Age, as nutrient absorption and immune function change over time.
- Baseline health status, which can influence how the body responds to supplementation.
- Dietary habits, which can either support or hinder the effectiveness of supplements.
Individuals should be informed about the scientific evidence surrounding each product. While some ingredients may show promise in boosting immune responses, others might not deliver the expected results. Awareness of these distinctions is key to responsible supplementation.